
The Medici Family’s Religion shaped their power and reputation in Renaissance Italy. Many wonder why religion mattered so much to a family known for banking, art, and politics.
Religion gave the Medici family control, respect, and influence. It helped them launch the careers of popes and support world-famous art.
Religion played a central role in the Medici family’s legacy, as it enabled them to become trusted advisers, supporters of religious art, and even leaders within the Catholic Church.
The Medici sponsored churches, funded grand religious artworks, and produced four popes, which significantly boosted their fame and power across Europe.
By exploring their religious actions and beliefs, you can learn how faith was a powerful tool for their family and for shaping Florence’s history. Their story extends beyond banking, reaching the heart of Renaissance society and the Catholic Church.
To truly understand their importance, it’s crucial to examine their faith and its lasting effects on their legacy.
The Role of Religion in the Rise of the Medici Family
The Medici family’s religious affiliation played a direct role in their rise to become one of the most powerful families in Florence. Their religious acts influenced politics, banking, art, and their place within the Catholic Church.
How the Medici Family Used Religion to Gain Political Power
The Medici family established relationships with church officials and utilized religious events as opportunities to form alliances. They funded religious festivals, churches, and public ceremonies, which helped them win trust and support from people and church leaders.
By controlling key religious offices and gaining the loyalty of priests and monks, the Medici strengthened their hold on Florence. Medici members joined religious orders and created networks that boosted their social status.
Medici marriages also linked the family to powerful religious and noble families across Italy. These alliances provided them with access to new political opportunities and maintained their centrality in local and church politics.
The Influence of the Catholic Church on Medici Wealth and Banking
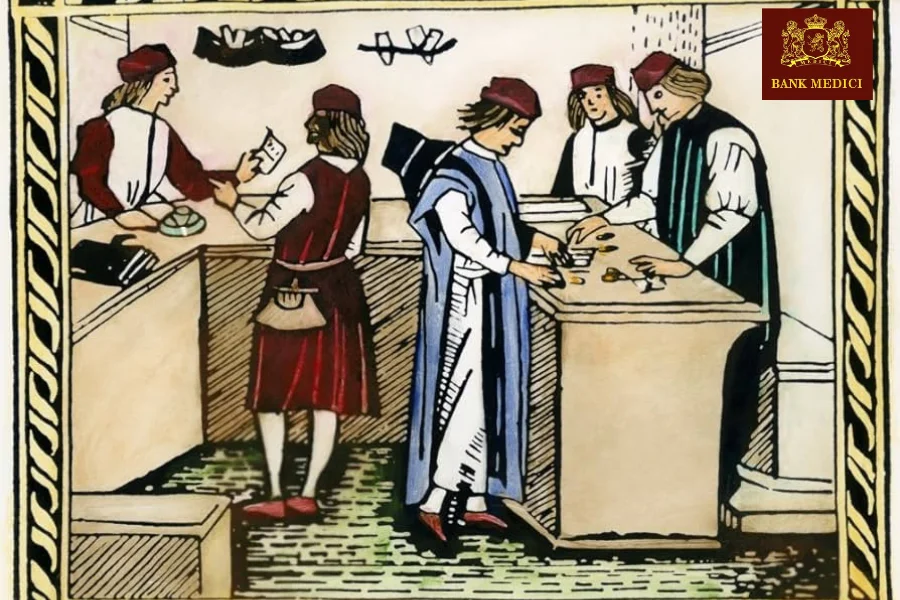

Medici wealth and banking success relied heavily on their connections within the church. The family ran the Medici Bank, one of Europe’s most important financial institutions during the Renaissance, and provided banking services directly to the Vatican and popes.
Close ties to the Catholic Church gave the Medici family special access to manage church funds and handle papal finances. This access increased their wealth and influence in European politics.
Medici bankers used their connections with bishops, cardinals, and popes to protect and expand their business. Church loans and donations from the Medici helped them win church favors and top positions in Florence and Rome.
Medici Patronage and Support for Religious Institutions in Florence
The Medici acted as leading patrons of religious institutions in Florence. They funded the building and restoration of many churches, monasteries, and convents, most notably the Florence Cathedral and San Lorenzo.
Religious art commissions flourished under their patronage. Artists like Botticelli, Donatello, and Michelangelo created religious paintings, sculptures, and architectural works for these sacred spaces.
This support was both an act of devotion and a display of power. Lavish religious art and architecture enhanced the Medici chapel as a family symbol, connecting their legacy to Florence’s spiritual life.
Papal Connections and the Rise of Medici Popes Leo X and Clement VII
The Medici family’s influence reached its peak with the election of two Medici popes: Leo X and Clement VII. Both men, born Giovanni and Giulio de’ Medici, used their positions as heads of the Catholic Church to advance their family’s power and protect their interests.
As popes, they guided church policy in ways that favored Florence and the Medici. They appointed family members and loyal supporters to high church offices and used papal resources for Medici projects.
Their rule shaped European religious reform, art patronage, and religious diplomacy. The Medici popes strengthened ties between Florence and Rome, granting the family spiritual authority and political power.
Religious Faith and Beliefs That Shaped the Medici Family Ambitions
Religious faith guided the Medici family’s daily lives and ambitions. They followed Catholic rituals and supported religious orders as part of their public image.
They funded religious charities and built chapels and tombs, showing commitment to spiritual traditions and family legacy. The Medici tombs and chapels became critical religious symbols in Florence.
Many members saw their power as a duty to serve God and society. Their blend of religious conservatism and support for new humanist ideas helped them bridge old traditions and changes during the Renaissance.
Religious Patronage and Artistic Legacy During the Renaissance

The Medici family’s religion shaped their legacy and the cultural history of Florence. Their religious patronage fueled artistic growth and left a visible mark on religious architecture and art.
Medici Family Patronage of Art and Artists in Florence
The Medici family became leading patrons of art and artists in Florence during the Renaissance. Their wealth from banking enabled them to sponsor famous names such as Michelangelo, Leonardo da Vinci, and Botticelli.

Cosimo de Medici and Lorenzo de Medici provided artists with financial support and political protection, enabling them to create works rich in religious symbolism and humanist themes.
Many projects the family commissioned celebrated religious devotion and the Medici legacy. They supported writers and philosophers, encouraging debates about faith and humanism.
The Medici viewed art as a means to express both power and piety, thereby linking their family to Florence’s spiritual heritage.
Religious Art Commissions and the Medici Family Chapels
The Medici family invested in religious art commissions to showcase their devotion and ties to the Catholic Church. They funded elaborate altarpieces and chapel decorations for Florence’s most important churches, including Santa Maria Novella and San Lorenzo.
Their art commissions often showed biblical scenes with members of the Medici family depicted as saints or donors. This practice connected their wealth and status to religious faith.
The Medici family chapels became significant spaces for both private worship and public ceremonies. Artists created frescoes, sculptures, and paintings that filled these chapels with images of spiritual power and family achievement.
These chapels also became burial places, reinforcing the family’s spiritual presence in Florence.
The Medici Chapel and Religious Symbolism in Renaissance Florence
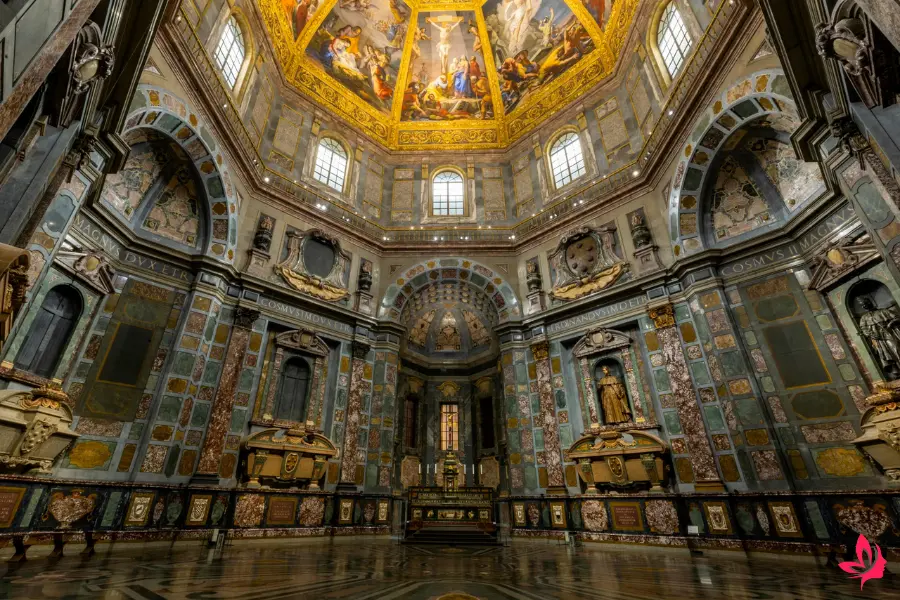

The Medici Chapel is a prime example of how the family utilized art and architecture to convey their religious and political influence. Built within the Basilica of San Lorenzo, this chapel exemplifies the Medici family’s close connection with the church and their utilization of spiritual symbolism.
The decoration features sculptures by Michelangelo that mix Christian symbols with themes of power and eternity. Statues of Medici dukes stand as reminders of the family’s role in Florence’s spiritual and civic life.
Religious imagery in the chapel celebrates resurrection and divine favor, tying the Medici family legacy to ideas of salvation. The use of light, marble, and grand tombs reinforces both religious faith and family pride.
How Humanism and Religion Intersected in Medici-Sponsored Art
Humanism—a movement that celebrates individual achievement and classical learning—was blended with religious ideas in Medici art commissions. Lorenzo de Medici encouraged artists and thinkers to combine stories from Christianity and ancient Greece or Rome.
Many works funded by the family show saints in realistic settings and include symbols of faith and classical wisdom. The Medici supported projects in which artists explored questions about free will, virtue, and the soul.
The result was art that honored the Catholic Church but reflected a broader view of humanity. The spread of humanist ideas made Florence a leading center of learning and religious innovation during the Renaissance.
Florence Cathedral and the Medici Influence on Religious Architecture
Florence Cathedral, also known as the Duomo, symbolizes the power and religious devotion of the Medici family. The family funded numerous building projects and renovations, supporting artists like Brunelleschi in the completion of the famous dome.
The Medici utilized their wealth and political connections to shape church policies and influence appointments within the Catholic Church. Their support helped make the cathedral a center for important religious ceremonies, including Medici weddings, papal visits, and major feasts.
Special chapels and tombs within the cathedral served as permanent reminders of the family’s religious and social significance. The Medici influence on church buildings made Florence a model city for spiritual and artistic achievement.
Medici Religion and Its Impact on Church Politics and Legacy

The Medici family’s religion shaped their role in Renaissance Florence. Their devotion, political ambitions, and partnership with the Catholic Church altered Italy’s church politics, art, and social structures.
Medici Influence on the Vatican and Religious Diplomacy
Medici family members played a decisive role in the Vatican, reaching the height of influence when Giovanni de’ Medici became Pope Leo X and Giulio de’ Medici became Pope Clement VII.
Their time as Medici popes gave Florence valuable political power and diplomatic advantages. By controlling high-ranking church offices, the Medici established alliances with other European rulers through religious diplomacy and their connections to the papacy.
These strong ties helped strengthen their position in Florence and across Italy. Through patronage of religious institutions and art, such as commissions for grand churches and cathedrals, the Medici helped shape the direction of the Papacy and the Catholic Church during the Renaissance.
Their influence on the Vatican was evident in bold reforms, policies, and support for artists and scholars, making them key figures in the history of the Church.
The Role of Medici Dukes in Religious Power Dynamics and Church Politics
The Medici dukes saw religion as more than faith. They used it to secure and legitimize wealth and political authority in Florence.
By aligning themselves with church leaders and funding large religious projects, the Medici enhanced their public image and spiritual authority. They built and restored important churches, such as San Lorenzo, and financed the construction of the Medici Chapel, which served as both a religious site and a family tomb.
These acts showcased their devotion and reinforced the dynasty’s role in both religious and civic life. The Medici used church politics to secure marriages and alliances with powerful European families.
They tied their legacy and power closely to Florence’s rise and prestige through religious patronage.
Religious Conflicts and Controversies Surrounding the Medici Family
The Medici family faced many religious controversies and challenges. Some critics accused them of using their spiritual authority for personal gain.
Powerful enemies sometimes attempted to discredit the Medici by portraying them as corrupt or heretical. During the rule of certain Medici popes, the Catholic Church experienced deep divisions and open conflicts with reformers.
These included financial scandals tied to indulgences and the tricky politics surrounding the Reformation. The Medici often responded by defending conservative religious values and seeking unity.
Their approach to religious conflicts sometimes led to tension between Florence and the Roman Catholic Church. This sparked debates over religious faith, church politics, and the true nature of their influence.
Medici Religious Ceremonies, Devotion, and Their Public Image
The Medici family carefully observed Catholic rituals and sponsored elaborate religious ceremonies, including major feasts and processions.
They supported Florence Cathedral and other sacred spaces. This devotion helped reinforce their credibility in the eyes of the public.
The Medici commissioned religious art for churches. They paid artists to capture critical spiritual moments in frescoes and sculptures.
These works became symbols of Medici spirituality. They served as lasting reminders of the family’s commitment to the church.
The Medici attended masses, supported religious orders, and built private chapels. These acts heightened their standing and strengthened ties with the city’s most influential religious institutions.
The Lasting Medici Legacy Through Religious Reform and Philanthropy
The Medici legacy continues in the religious reform and acts of charity they inspired. Some Medici leaders supported education, religious orders, and care for the poor in Florence.
Their foundations built schools, hospitals, and other religious institutions that served the city for centuries. The Medici played a pivotal role in shaping Florence into a hub for art and spiritual growth.
Their support for humanism and patronage encouraged cultural change. They linked religious belief with new ideas from the Renaissance.
Frequently Asked Questions
The Medici family played a pivotal role in Florence’s history through their influence in religion, politics, and the patronage of the arts. Their faith profoundly shaped their public image and private actions, influencing the cultural and religious life of Italy.
What religion were the Medici?
The Medici family was Christian and followed Roman Catholicism. Their religious beliefs influenced their decisions as rulers and art patrons in Florence.
Was the Medici family Catholic?
Yes, the Medici were devoted Catholics. Their influence helped shape the Catholic Church and its art, with several family members rising to high-ranking church positions, including popes such as Pope Leo X and Pope Clement VII.
What religion was Catherine de Medici?
Catherine de’ Medici, a member of the Medici family, was also Roman Catholic. She brought her Catholic faith to France when she became Queen Consort and later Queen Mother.
What happened to the Jews in Florence?
During the Medici rule, attitudes towards Jews changed at different times. At certain times, the Medici tolerated and protected the Jewish community.
At other times, pressures increased and restrictions grew, depending on the political climate.
What was the dark side of the Medici family?
The Medici used their influence and wealth to gain control of Florence. They faced accusations of corruption, nepotism, and sometimes violence to remove rivals and secure their position as rulers.
Power struggles led to betrayal and assassinations within and outside the family.
How many Jews are in Florence?
Today, Florence has a small Jewish community. The exact number changes, but it is much smaller now than during the Renaissance period.
What church did the Medici build?
The Medici family sponsored the building and decoration of several churches in Florence. One of their most important contributions was to the Basilica di San Lorenzo, which contains the Medici Chapels.
These spaces were designed as resting places for members of the Medici family.
Where did the Medici family get rich from?
The Medici gained their wealth from banking. Their bank became one of the most powerful in Europe, and they served as bankers to the pope.
Their financial power helped them rise to political leadership in Florence.
What church was Medici killed in?
Giuliano de’ Medici was killed during Mass in the Florence Cathedral, also known as the Duomo or Santa Maria del Fiore. This event was part of the Pazzi Conspiracy in 1478.
Does the Medici family still exist today?
The original Medici dynasty ended in the 18th century.
People with the Medici name may still exist, but the family no longer holds power or influence.



 Leonardo Bianchi,
the creator of Leonardo da Vinci's Inventions.
Thank you for visiting
Leonardo Bianchi,
the creator of Leonardo da Vinci's Inventions.
Thank you for visiting