The Medici family names are often linked with power, art, and political intrigue. It can be challenging to keep track of the key individuals in their extensive history.
You may wonder which relatives truly shaped the family’s legacy, and which names are important to remember. This overview will help you easily identify the most influential Medici, so you understand how each person left their mark.
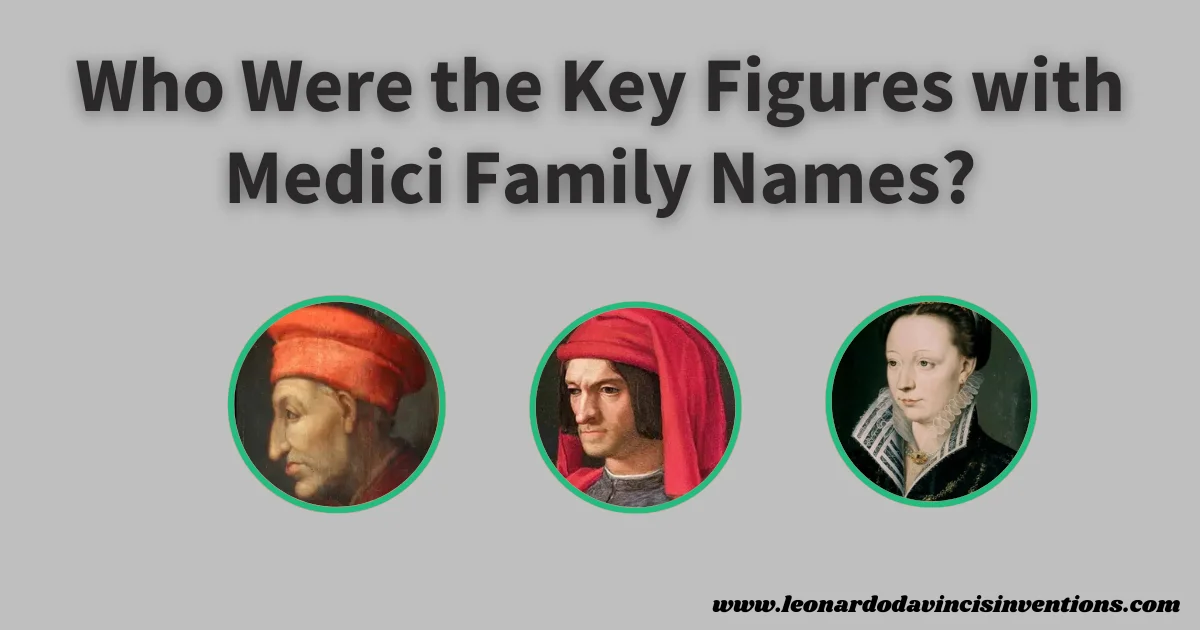
Cosimo de’ Medici, Lorenzo de’ Medici, and Catherine de’ Medici were among the most significant figures bearing the Medici name, each playing a pivotal role in the rise of the family’s wealth and influence.
Other major members include Cosimo I, Francis I, and several popes such as Leo X and Clement VII.
Explore the connections between these names and the arts, politics, and religion through the Medici family tree and their remarkable history.
The Rise of the Medici Family in Florence and Tuscany
The Medici family transformed the history of Florence and Tuscany by establishing a powerful banking dynasty and exerting influence across politics, the arts, and the Church.
Their rise began with wealth and expanded through strategic marriages, political maneuvering, and support for artists and scientists.
Medici Family Names and Their Banking Dynasty Origins

The Medici family first became wealthy through successful banking. Giovanni di Bicci de’ Medici set the foundation for the Medici Bank in the late 1300s.
This bank soon became one of the most powerful in Europe. It managed accounts for popes, kings, and major city-states.
Giovanni’s son, Cosimo de’ Medici, expanded the family’s banking operations while also strengthening ties with Florence’s elite. Cosimo managed money carefully and supported neighbors and politicians, which increased the Medici’s wealth and influence.
By offering loans and funding public works, the family won loyalty and respect among both citizens and rulers. Their banking power let the Medici family become the chief financiers of the Papacy and other Italian states.
Banking contracts, investments, and financial innovation helped turn them into a true banking dynasty.
The Medici Family Tree and Noble Family Connections
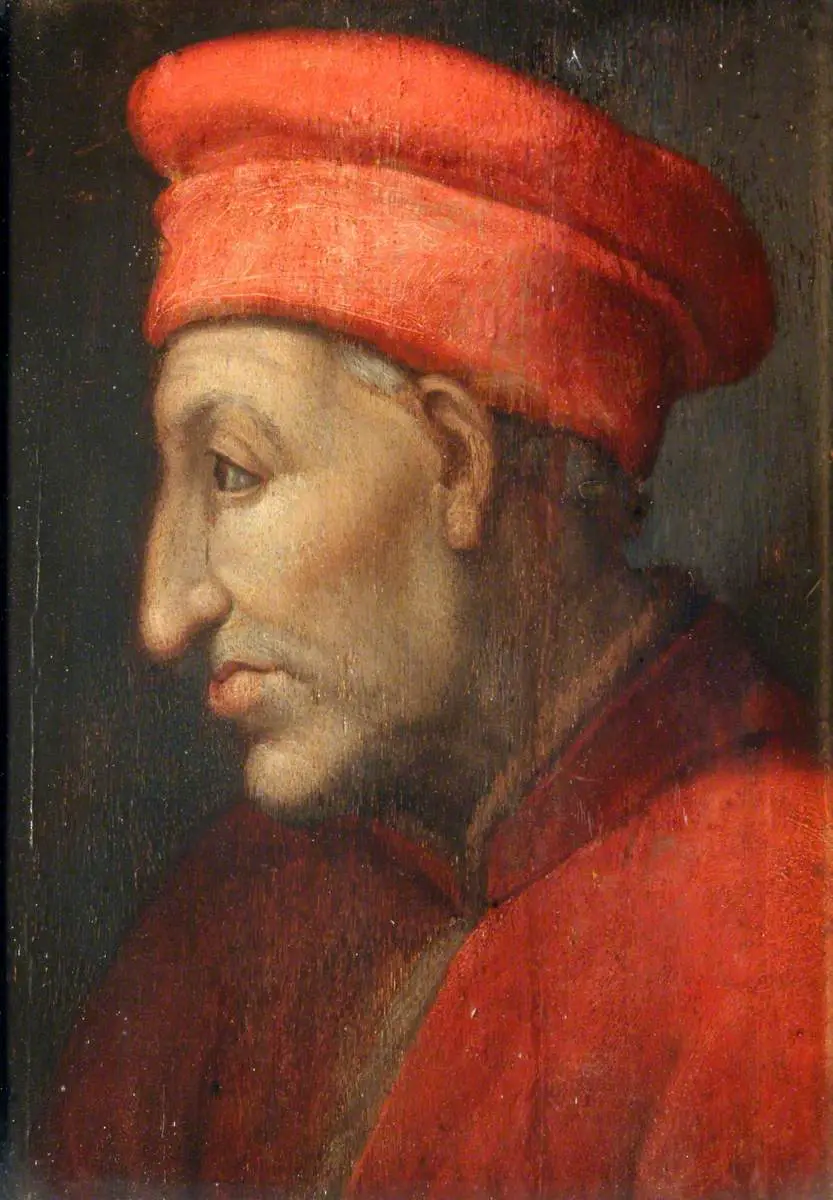

The Medici family tree includes famous names such as Cosimo de’ Medici (Cosimo the Elder), Piero de’ Medici, Lorenzo de’ Medici (Lorenzo the Magnificent), and Catherine de’ Medici. Medici family members became popes, queens, and grand dukes, cementing their status among European royalty.
They strengthened family lineage through strategic marriages and alliances. For example, Catherine de’ Medici became Queen of France, and several members of the Medici family married into other ruling families.
The Medici coat of arms became a symbol of the noble family’s reach across Italy and Europe. These alliances made the Medici family a part of the broader network of European royalty and monarchs.
Their descendants included kings, grand dukes, and popes, which helped secure their legacy for centuries.
Florence, Tuscany, and the Republic of Florence’s Political Power
The rise of the Medici family in Florence led to their control of the Republic of Florence. Cosimo de’ Medici and his heirs mainly ruled behind the scenes, but their influence was decisive.
They utilized money and allies to outmaneuver their rivals and exert control over both politics and the economy. The Medici transformed Florence into a powerful city-state and the center of the Renaissance.
Their patronage of the arts attracted masters like Michelangelo and Leonardo da Vinci. Medici rulers later became Grand Dukes of Tuscany, expanding their power beyond Florence to encompass the broader region of Tuscany.
Their leadership left a lasting impact through monuments, libraries, and palaces, such as the Palazzo Medici. They shaped the culture and political history of both Florence and Tuscany.
Key Rulers and Influencers with Medici Family Names
The Medici family became one of the most powerful and influential noble families in Italian history. Through power consolidation, banking, art patronage, and strategic alliances, they shaped the Republic of Florence and impacted European royalty.
Cosimo de’ Medici and Giovanni di Bicci de’ Medici: Founders of Power
Giovanni di Bicci de’ Medici started the Medici family’s rise by founding the family’s influential banking dynasty in Florence. His careful management and investments made the Medici Bank one of the most important banks in Europe.
Giovanni’s leadership set the groundwork for the family’s increasing wealth and reputation. Cosimo de’ Medici, also called Cosimo the Elder, expanded on his father’s success.
He acted as the unofficial ruler of Florence, exercising tremendous political power behind the scenes. Using an extensive network, Cosimo de’ Medici supported artists and thinkers, helping to spark the Renaissance.
Lorenzo de’ Medici and Piero de’ Medici: Art Patronage and Renaissance Leadership

Lorenzo de’ Medici, known as “Lorenzo the Magnificent,” was a powerful ruler who led Florence during the Renaissance’s peak. He supported leading artists such as Michelangelo and Leonardo da Vinci, transforming Florence into a cultural hub of influence.
Under his guidance, the Medici Palace became known for hosting poets, philosophers, and scientists. Piero de’ Medici, his son, did not enjoy the same level of respect.
He lost control of Florence due to unpopular decisions and conflicts, which led to the end of the family’s rule for a period.
Catherine de’ Medici and the Medici Legacy in European Royalty
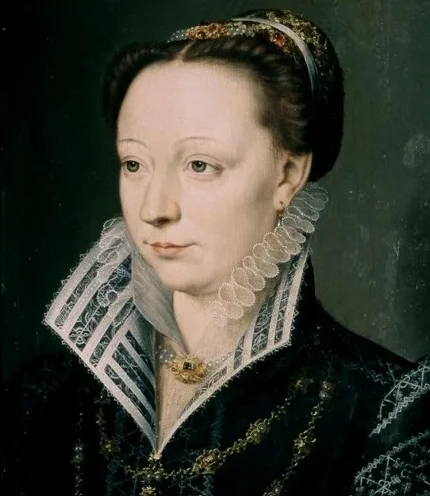

Catherine de’ Medici‘s marriage brought the Medici lineage into the royal families of France. As queen, she influenced French politics during times of religious conflict and court intrigue.
Her children became kings and queens, spreading the Medici heritage in European royalty. Catherine’s background in the Medici family allowed her to bring Italian culture and artistic achievements to the French court.
She strengthened the Medici legacy through strategic marriages and alliances, extending their reach far beyond Tuscany and Florence. The impact of the Medici family tree is evident in the royal houses that followed.
The Medici Family’s Cultural Impact and Enduring Legacy
The Medici family shaped Renaissance Florence, becoming powerful rulers, prominent bankers, and key supporters of the arts and sciences.
Through patronage, dynastic intrigue, and political power, the Medici family left an enduring mark on Italian history and world culture.
Medici Patronage of the Arts: Michelangelo, Leonardo da Vinci, and More
Medici art patronage fueled the Renaissance’s flowering in Florence. Cosimo de’ Medici and Lorenzo de’ Medici, both famous rulers, commissioned artists such as Michelangelo, Leonardo da Vinci, Botticelli, and Donatello.
Their support helped launch masterpieces and elevate Florence as a leading center of culture. Lorenzo de’ Medici, known as “the Magnificent,” personally fostered young Michelangelo, allowing him access to the Medici Palace and collection.
The Medici family’s legacy in art is visible in landmarks such as the Medici Chapel, featuring its grand Medici tombs, and the Medici Library. The Medici also sponsored scientific studies and the translation of ancient texts, thereby advancing Western knowledge.
Medici Popes, Dukes, and Grand Dukes of Tuscany: Monarchs and Papacy

Members of the Medici family tree became significant figures in European royalty and the Catholic Church. Four Medici popes—Leo X, Clement VII, Pius IV, and Leo XI—rose from this noble family, guiding the Church during crucial periods of religious change and dynastic struggle.

Medici popes used their wealth and influence to support art, architecture, and the Medici coat of arms in Rome. The Medici dynasty also produced dukes and Grand Dukes of Tuscany, ruling the region as monarchs for generations.
Their leadership transformed Florence and Tuscany, consolidating power while creating a lasting legacy of monuments, art, and scholarly achievements that extended across Italy and Europe.
Medici Influence on Culture, Medici Monuments, and Medici in Popular Culture
Medici’s influence on culture spans beyond art and politics. The family’s name adorns historic sites, such as the Palazzo Medici and the Medici Chapel.
Their funerary monuments stand as symbols of power and taste, while their archives preserve centuries of political and personal history. In recent years, Medici restoration projects have revived interest in the family’s heritage.
The Medici appear in popular culture, including TV shows, films, and literature, fueling fascination with their wealth, scandals, and dynastic intrigue. Alliances through marriage further intertwined the Medici genealogy with European royalty, deeply embedding their name in world history.
Frequently Asked Questions
The Medici family shaped Florence and European politics for centuries. Many people are curious about their current heirs, their wealth, hidden secrets, and the decline of their power.
Are there any Medici families today?
There are no direct male heirs from the historic Medici family. The original branch ended in the 1700s.
While some families in Florence have the Medici name, they are not related to the famous dynasty.
Who is the most famous Medici?
Lorenzo de’ Medici, known as Lorenzo the Magnificent, is often seen as the most famous. He led Florence during the Renaissance and supported artists like Michelangelo and Botticelli.
People also know him for his political skills and leadership.
Who inherited the Medici fortune?
After the death of Anna Maria Luisa, the last direct descendant of the Medici, the family’s fortune and art collection were left to the Tuscan state. She made an agreement that ensured the Medici art would remain in Florence forever.
What was the Medici family called?
The family is commonly referred to as the House of Medici. Members included names like Giovanni di Bicci de’ Medici, Cosimo de’ Medici, and Lorenzo de’ Medici.
Their full name in Italian was “de’ Medici di Cafaggiolo,” more on key family names.
What was the dark side of the Medici family?
The Medicis employed bribery, marriage, and violence to acquire and maintain power. Political enemies sometimes faced exile or even death. Family members became involved in scandals and several murders.
Are there any living descendants of Mary, Queen of Scots?
Mary, Queen of Scots, was not part of the Medici family. Many European royals today can trace their bloodlines back to her.
How did the Medicis lose their money?
Later, the Medicis mismanaged the family’s banking business. Wars, political troubles, and overspending drained their fortune. By the 18th century, most of their wealth had been depleted.
Who was the last legitimate heir to the Medici dynasty?
Anna Maria Luisa de’ Medici was the last legitimate heir. She died in 1743, ending the main line of the family.
How much would the Medici be worth today?
It is hard to give a direct value. In today’s money, the Medicis could have been worth billions. Their banking, land holdings, and art collection made them among the wealthiest families in Europe.
Which Medici died of syphilis?
Alessandro de’ Medici, Duke of Florence, is rumored to have suffered from syphilis before his assassination in 1537.
However, historians remain uncertain about the medical details from that time.



 Leonardo Bianchi,
the creator of Leonardo da Vinci's Inventions.
Thank you for visiting
Leonardo Bianchi,
the creator of Leonardo da Vinci's Inventions.
Thank you for visiting