
How did Leonardo da Vinci contribute to the Renaissance?
Many people know his name, but few understand how much he shaped art, science, and technology.
If you have ever wondered why Leonardo is mentioned in textbooks and museums, you will find out how his mind changed the world.
Leonardo da Vinci made remarkable contributions to painting, engineering, architecture, anatomy, and even inventions ahead of his time.
His thirst for knowledge and deep curiosity led him to revolutionize art and science, setting new standards for creativity and research during the Renaissance.
By learning more about him and his works, you can explore how his masterpieces and discoveries still impact our lives today.
Leonardo da Vinci’s Artistic Contributions to the Renaissance
Leonardo da Vinci set new standards for painting by combining science, engineering, and art. His work shaped the direction of the Renaissance by defining the High Renaissance art period and promoting innovation in technique and storytelling.
Leonardo da Vinci and the Birth of High Renaissance Art
Leonardo da Vinci played a vital role in the rise of High Renaissance art by blending realism with creativity. He set himself apart through careful observation of nature and advanced studies in anatomy.
His figures appeared lifelike and expressive. Leonardo joined technical skill with imagination, raising expectations for artists of his time.
His use of perspective, shading, and light helped create accurate and emotionally powerful art. This approach allowed him to merge scientific study with painting, inspiring peers and future generations.
Because of his influence, High Renaissance artists began to pay more attention to human anatomy, emotion, and natural backgrounds.
Masterpieces That Defined an Era: Mona Lisa, The Last Supper, and Salvator Mundi
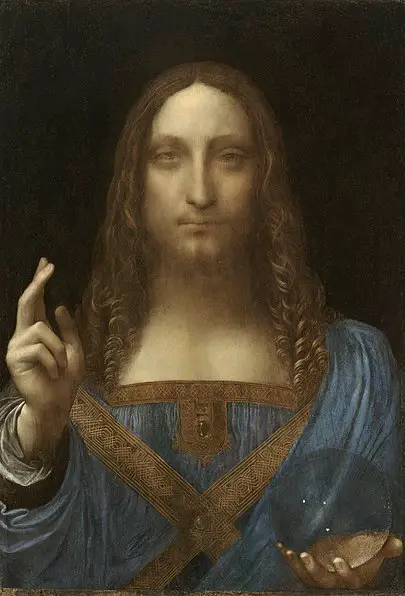

Leonardo’s Mona Lisa is famous for her mysterious smile and delicate use of light and shadow. The painting’s lifelike detail and emotional depth made it revolutionary.
Leonardo arranged the figures in The Last Supper to highlight drama, emotion, and each Apostle’s unique reaction. This set a new standard for storytelling in art.
Another key work, Salvator Mundi, showcases da Vinci’s skill in combining spiritual themes with precise detail. These masterpieces showed how art could stir emotions and tell complex stories, not just capture appearances.
Leonardo da Vinci helped define what Renaissance painting could achieve, influencing every painter who followed him.
Revolutionizing Painting Techniques: Innovation in Art and Optics
Leonardo da Vinci revolutionized painting through technique. He advanced sfumato, blending colors and tones to create soft edges and realistic light effects.
This innovation made his subjects appear more natural, with skin, cloth, and hair that seemed to glow from within. He also studied optics, examining how light and shadow work in nature.
By applying his understanding of physics and observation, he made scenes look three-dimensional and full of life. His discoveries linked scientific study with visual art, bringing painting techniques closer to realism.
The Role of Storytelling and Writing in Leonardo’s Artistic Vision
Writing and storytelling were central to Leonardo’s vision as a painter. He filled notebooks with drawings, story ideas, and notes on everything from engineering to anatomy.
His creative process included planning scenes, sketching character poses, and shaping the story behind each painting. By arranging figures, expressions, and gestures, Leonardo brought complex emotions and narratives to life on canvas.
This focus on storytelling made his art meaningful and beautiful. Through his studies and writing, da Vinci’s works delivered layered stories that viewers could interpret and explore.
Legacy in Western Art History: How Leonardo Shaped Future Generations
Leonardo da Vinci’s artistic legacy still shapes Western art history. He showed later artists how painting could combine beauty, technical mastery, and deep meaning.
His focus on the scientific method, anatomy, and perspective pushed art forward. Da Vinci’s sketches and inventions influenced art and fields like mechanical engineering and hydrodynamics.
His legacy encouraged intellectual curiosity and observation in painting, urban planning, and medical physics. Leonardo’s influence paved the way for centuries of innovation and artistic excellence.
Leonardo da Vinci’s Scientific and Engineering Innovations
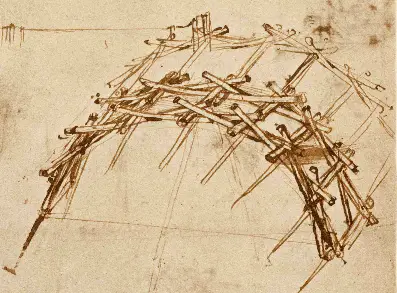
Leonardo da Vinci’s investigations reached across engineering, anatomy, and city planning during the High Renaissance. His careful observation and inventive mind gave rise to ideas and discoveries that shaped art, science, and knowledge in the Western world.
Leonardo’s Interdisciplinary Contributions: Bridging Art, Science, and Engineering
Leonardo da Vinci blended art and science in groundbreaking ways. He believed understanding how things work was essential for creating better paintings and inventing new machines.
In his notebooks, he combined drawing, writing, and experimentation. These books show his fascination with geometry, optics, and mechanics.
His paintings, including the Mona Lisa and The Last Supper, display artistic expertise and a deep understanding of anatomy and physics. This mix of disciplines allowed Leonardo to pioneer new methods in painting and invent devices that were centuries ahead of their time.
By bridging art and science, he helped shape the Renaissance idea of a true “universal genius.”
Anatomy and Medical Physics: A Natural Genius Explores the Human Body
Leonardo’s curiosity about the human form led him to study anatomy deeply. He dissected humans and animals, making hundreds of precise sketches of bones, muscles, nerves, and organs.
His anatomical drawings, including the well-known Vitruvian Man, show ideal human proportions. These studies improved his paintings and advanced medical physics and biomedical studies.
Leonardo’s exploration of the heart, blood vessels, and how the body moves went further than most doctors of his era. Though he never published his work, historians agree that his research offered new insights into medicine and the scientific study of anatomy.
He combined careful observation and early scientific method in his approach.
Mechanical Engineering and Hydrodynamics: Inventions Ahead of Their Time
As an inventor, Leonardo da Vinci designed machines far ahead of the Renaissance. He sketched concepts for a helicopter, parachute, armored vehicle, and various mechanical devices for lifting and transporting.
These inventions show his expertise in mechanical engineering and his creative thinking. Leonardo also studied the movement of water, or hydrodynamics.
He designed pumps, water wheels, and canal systems to manage water in towns and cities. Many of these ideas remained visions on paper, but some inspired later generations of engineers.
His notebooks are filled with gears, levers, and cams, showing how he brought scientific ideas into practical engineering. Many of his plans were not built in his lifetime but proved influential later.
Urban Planning and Cartography: Visionary Ideas for Renaissance Cities
Leonardo’s vision for cities included wide, clean streets and organized neighborhoods to improve health and movement. He drew detailed city plans with separate areas for foot traffic, carts, and waterways.
He helped shape modern urban planning ideas and advanced the art of cartography by drawing precise maps and topographical sketches.
These maps often included natural features, roadways, and buildings. Leonardo’s work helped leaders better understand and visualize their territories.
His approaches to city design reflected his desire to solve problems like disease and overcrowding. His innovations set standards for city layouts and civic engineering during the Renaissance.
Early Scientific Method and Intellectual Curiosity in Leonardo’s Work
Leonardo’s work shows the beginnings of the modern scientific method. He believed direct observation and repeated experiments were the best ways to learn about nature.
His notebooks contain careful notes, step-by-step tests, and critical thinking. This intellectual curiosity drove Leonardo to challenge accepted beliefs.
He wrote about the need for evidence over tradition and wanted to understand the cause and effect of every phenomenon. This early use of experiment, observation, and logic set him apart from many scholars of his age.
Leonardo helped revolutionize art and science for future generations. His legacy stands as a foundation for cross-disciplinary study and the evolution of knowledge in Western art history.
The Broader Impact of Leonardo da Vinci on Renaissance Thought and Knowledge
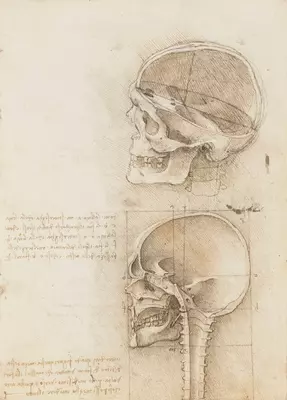
Leonardo da Vinci impacted the Renaissance through bold innovations, bridging art and science in new ways. His natural genius pushed the boundaries of engineering, philosophy, anatomy, and invention.
Philosophy and the Evolution of Knowledge During the Renaissance
Leonardo da Vinci shaped Renaissance philosophy by pushing for observation over blind acceptance of tradition. He insisted on questioning what was already known, which led him to challenge the ideas of ancient scholars and Church doctrine.
Leonardo centered learning on experimentation and direct study, which sparked growth in anatomy and optics.
His notes, sketches, and scientific studies encouraged evidence and careful observation. Leonardo’s thinking influenced other thinkers to see the world more logically and scientifically.
The Renaissance saw a rise in the scientific method due to its clear focus on testing and proof. As a result, the fields of philosophy and science changed in lasting ways during the High Renaissance.
Leonardo as an Inventor: Innovation Rooted in Observation of Nature
Leonardo is known as an inventor who closely studied the natural world. His notebooks contain sketches and ideas for machines such as a bicycle, a flying device, and early versions of the helicopter.
Many of these never became fundamental inventions in his lifetime, but his ideas reflected creative problem-solving and a deep curiosity about how things work. Leonardo’s inventions, like his designs for military machines and water pumps, show an early understanding of engineering and hydrodynamics.
His contributions to engineering and scientific study sparked future innovation. He believed that mimicking nature could help invent useful machines.
His focus on observation helped him understand human anatomy and animal motion. This approach improved the way later inventors and scientists explored new technologies.
Leonardo’s natural genius as an inventor still inspires engineers and inventors today.
Cross-Disciplinary Approach: How Leonardo Revolutionized Art and Science
Leonardo da Vinci is the classic example of a “Renaissance man.” He revolutionized art and science by combining disciplines to make discoveries.
His paintings, like the Mona Lisa and The Last Supper, show mastery of anatomy, perspective, and light.
Leonardo used scientific techniques to study muscles and facial expressions. This helped his masterpieces feel lifelike.
He applied mathematical ratios and optical science to improve realism in his art. His scientific study led to better art, and his artistic mind brought creativity to engineering.
Writing and Documentation: Preserving Leonardo’s Ideas for Posterity
Leonardo da Vinci recorded his observations and documented every part of his studies. His notebooks cover topics ranging from cartography and architecture to medical physics.
He wrote in mirror script, possibly to keep his work private or to make writing easier as a left-hander. These notebooks are important artifacts from the Renaissance because they preserve early forms of the scientific method.
They offer step-by-step explanations, sketches, and personal reflections. Many later engineers and scientists learned from Leonardo’s habit of documentation.
His detailed notes allowed people to study his advances in anatomy, optics, and mechanical design hundreds of years later.
Writing and organizing his ideas helped make Leonardo’s legacy in Western art history possible.
The Enduring Legacy of Leonardo da Vinci in Renaissance Culture and Beyond
Leonardo’s influence on Renaissance culture endures in both art and science. His masterpieces, such as the Mona Lisa and Salvator Mundi, remain icons of Western art history.
Museums and researchers still study his notebooks to understand his role in shaping engineering, innovation, and storytelling. He inspired a tradition of intellectual curiosity and the pursuit of knowledge.
Leonardo’s interdisciplinary contributions made it common for people to work across fields. Today, people remember him not just as a painter, but as a symbol of creativity and human potential.
His legacy extends into urban planning, biomedical studies, architecture, and modern design. Leonardo da Vinci’s impact on the Renaissance still shapes scholarship and creativity worldwide.
Frequently Asked Questions
Leonardo da Vinci is known for his art, science, engineering, and anatomical work during the Renaissance. He left a lasting mark on both creative and scientific fields and inspired future generations in many areas.
What were the contributions of Leonardo da Vinci to the Renaissance?
Leonardo made key advances in painting, with works like the Mona Lisa and The Last Supper. He also recorded detailed studies of anatomy and engineering in his notebooks.
Although not built in his lifetime, his inventions and scientific sketches showed new ways of thinking and learning in the Renaissance.
Why is Leonardo da Vinci considered a Renaissance person?
Leonardo da Vinci is called a “Renaissance man” because he excelled in many areas, including art, science, engineering, and anatomy. He blended creative talent with scientific study, making him an example of the well-rounded thinker valued during the period.
His curiosity led him to study everything from painting to designing machines.
How did art impact the Renaissance?
Art in the Renaissance reflected new ideas about people, nature, and the world. Artists studied anatomy, perspective, and light to create more realistic paintings and sculptures.
Their work helped spread ideas and inspired interest in science and discovery.
Which painter was active during the Renaissance?
In addition to Leonardo da Vinci, other well-known Renaissance painters were Michelangelo, Raphael, and Sandro Botticelli. These artists are famous for changing how people thought about art with their techniques and subjects.
What was the influence of Leonardo da Vinci?
Leonardo’s influence reached many fields, such as engineering, architecture, anatomy, and philosophy. His ability to mix science with art inspired others to explore and learn in new ways.
This overview of his contributions shows that he played a big role in shaping the culture of the Renaissance.
What started the Renaissance period?
The Renaissance began in Italy in the late 1300s. It was sparked by renewed interest in classical learning from ancient Greece and Rome, the growth of cities, and support from wealthy patrons for art and science.
What else was Leonardo da Vinci famous for?
Leonardo was also known for his scientific observations, engineering designs, and detailed anatomical drawings. His notebooks were full of studies on flight, water, and mechanics.
He also created plans for machines like helicopters and tanks.
Who were the inventors of the Renaissance?
Besides Leonardo, important inventors included Johannes Gutenberg, who made the printing press, and Galileo Galilei, who improved the telescope. These inventors changed communication, science, and technology during the era.
What contributions did Raphael make to the Renaissance?
Raphael was known for his clear, balanced paintings and work on the Vatican’s rooms, called the Stanze di Raffaello. His artwork, mainly portraits and religious scenes, contributed to new styles and standards in painting.
What is Leonardo da Vinci’s legacy today?
Leonardo’s legacy continues in both art and science. His paintings remain celebrated and studied worldwide.
People still admire and teach his approach to learning. As explained in this biography on Britannica, he combined imagination with careful observation and experimentation.

 Leonardo Bianchi is the founder of Leonardo da Vinci Inventions & Experiences, a travel and research guide exploring where to experience Leonardo’s art, engineering, and legacy across Italy and Paris.
Leonardo Bianchi is the founder of Leonardo da Vinci Inventions & Experiences, a travel and research guide exploring where to experience Leonardo’s art, engineering, and legacy across Italy and Paris.