The Medici Family Line influenced Renaissance art and culture in ways that fascinate people today.
If you want to understand how art and power became closely linked, you are in the right place.
This post examines their impact on creativity and society, presenting compelling stories about their role in shaping history.
The Medici family utilized their wealth to support artists, construct stunning buildings, and foster innovative ideas, thereby shaping the course of European art and culture.
Their support helped famous figures like Michelangelo and Leonardo da Vinci create some of their best work.
Their legacy remains visible in Florence and other parts of Italy, drawing visitors and scholars from around the world.
Many people want to know what made the Medici family so powerful and why their support was so important during the Renaissance.
By looking at how they influenced painting and architecture, you will see how their choices impacted culture.
Origins and Rise of the Medici Family Line in Florence
The Medici family started as merchants and bankers in Florence.
They became one of the most powerful families in Renaissance Europe.
For centuries, their financial strength and political strategy shaped Florence’s culture, art, and politics.
The Medici Family Tree and Early Banking Empire

The Medici family tree begins with Giovanni di Bicci de’ Medici, who established the Medici Bank in the late 14th century.
This bank soon became the largest in Europe.
Through careful business planning and partnerships, Giovanni set the groundwork for the Medici dynasty’s rise.
Table: Early Medici Family Tree
| Name | Role | Date |
|---|---|---|
| Giovanni di Bicci | Founder, Banker | 1360–1429 |
| Cosimo de’ Medici | Son, Political Leader | 1389–1464 |
| Lorenzo the Magnificent | Grandson, Art Patron | 1449–1492 |
Their banking empire provided the Medici family with the means to network with influential leaders in Italy and beyond.
With strong connections and financial security, the Medici gained significant influence in Florence.
Cosimo de’ Medici and the Foundation of Medici Wealth and Power

Cosimo de’ Medici, known as Cosimo the Elder, expanded the family’s wealth and reputation.
He used his banking fortune to gain power in Florence while remaining out of the public eye.
Cosimo funded churches, public buildings, and artists.
This patronage helped the family gain loyalty among the people of Florence.
Cosimo built alliances with both merchants and politicians.
His careful approach protected the family from rivals and made the Medici name trusted in the city.
Cosimo’s actions marked the beginning of Medici control, setting the stage for future generations to lead Florence.
Political Dynasty: Medici Influence on the Republic of Florence

The Medici family transformed Florence from a simple republic into a city-state dominated by a single powerful family.
Under Cosimo and later Lorenzo de’ Medici, the Medici’s political dynasty used influence, not formal titles, to direct Florence’s government decisions.
Lorenzo de’ Medici became a key figure during the Italian Renaissance, famous for supporting artists and thinkers.
The Medici supported Renaissance art, culture, and humanism.
Their influence shaped the city’s future and secured their family’s legacy as “uncrowned rulers” of the Medici political dynasty.
Medici Marriage Alliances and Expansion of Political Power
The Medici family utilized marriage alliances to establish connections with European royalty and noble families.
Strategic marriages, such as Catherine de’ Medici’s union with the King of France, helped the Medici expand their reach beyond Florence.
These marriage alliances brought new political power and wealth.
Medici queens and popes used their family connections to influence Italian and European affairs.
These ties meant the Medici family’s legacy continued through influential in-laws and descendants of Medici marriage alliances.
Florence Politics and the Medici Dynasty Rise
Florence’s politics were shaped by rival families and shifting alliances.
The Medici family used their banking wealth to win friends and silence enemies.
They built the Medici Palace to symbolize their family’s place in the city.
By controlling the financial and political systems, the Medici dynasty’s rise transformed the governance of Florence.
Wealth, family strategy, and political influence turned the Medici into Florence’s most important rulers.
Medici Patronage and Contributions to Renaissance Art and Culture
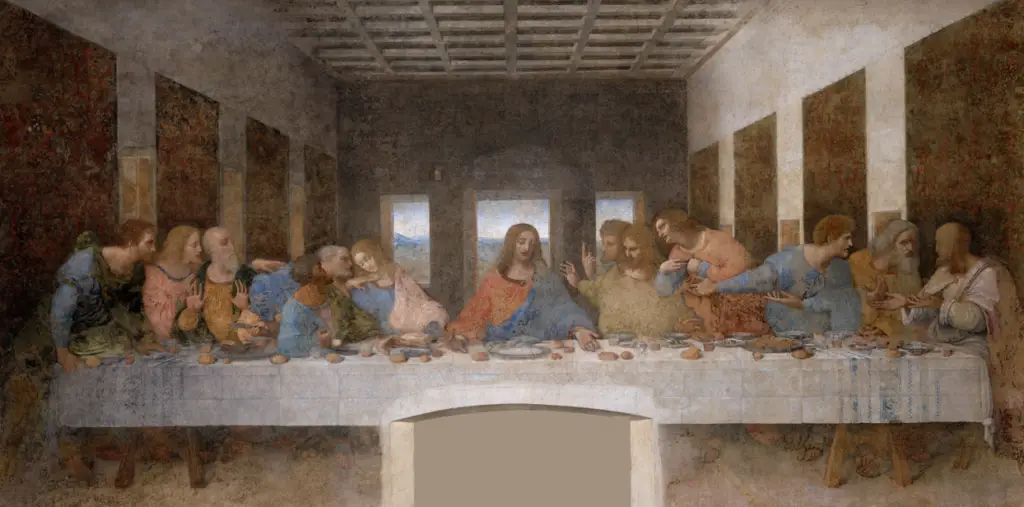

The Medici family significantly influenced the Italian Renaissance by leveraging their wealth, political power, and influence to support artists and thinkers in Florence.
Their support for painters, sculptors, scientists, and architects sparked changes that profoundly impacted Renaissance art and culture.
Lorenzo de’ Medici’s Role in Supporting Art and Artists
Lorenzo de’ Medici, known as “Lorenzo the Magnificent,” played a significant role in nurturing art and culture in Florence.
As the head of the Medici banking family, he utilized his fortune to support emerging artists, including Leonardo da Vinci, Michelangelo, and Botticelli.
Lorenzo opened his gardens to young sculptors, allowing them to train and learn from established masters.
He hosted scholars and poets at his court and funded workshops where artists could try new techniques.
This commitment fostered an atmosphere that encouraged creativity.
Lorenzo’s patronage enabled the creation of some of the most famous Renaissance art, such as Botticelli’s “The Birth of Venus.”
Medici Family Patronage of Renaissance Art and Culture
The Medici family’s influence on Renaissance culture extended beyond a single generation.
Members of the Medici dynasty, starting with Cosimo de’ Medici, bought and commissioned art for churches, palaces, and public spaces across Florence.
Their banking empire provided the resources to back large projects that would otherwise be impossible.
They supported poets, philosophers, and scientists, as well as visual artists.
This kind of broad patronage turned Florence into a key center of the Renaissance.
Their support funded or inspired many masterpieces, shaping the city’s look and defining its spirit.
Medici Palace as a Center of Artistic Innovation
Medici palaces served as gathering places for artists, architects, and intellectuals.
These buildings were not only luxurious homes but also hubs for creative exchange and display.
Architects like Michelozzo designed the Medici Palace with open courtyards and grand rooms to show art collections and promote dialogue.
Key features of the Medici Palace included:
- Display of commissioned sculptures and paintings
- A library that collected important works of science and literature
- Rooms dedicated to music and performances
The palace’s welcoming atmosphere let inventors and artists share new ideas and promote artistic breakthroughs.
The Medici coat of arms became a powerful symbol, often used in commissions, signaling the family’s support for the arts.
Medici Contributions to Art and Science During the Italian Renaissance
The Medici family legacy in Florence included strong support for both art and science.
They gave steady financial help to projects such as Leonardo da Vinci’s anatomical studies and Galileo Galilei‘s work.
Some Medici rulers established botanical gardens and constructed observatories for scientists.
The Medici family also amassed a collection of manuscripts, ancient texts, and rare books, which ultimately led to the establishment of the Laurentian Library.
By backing both creative and scientific exploration, they promoted a balanced vision of knowledge that pushed the Renaissance forward.
Their patronage of science and art helped make Florence a leading center for discovery and culture.
The Impact of Medici Popes on Art and Religious Culture
Medici popes strengthened the connection between the Catholic Church and Renaissance art.
Pope Leo X and Clement VII, both from the Medici family, funded the work of major artists in Rome and Florence.
For example, Leo X commissioned Raphael to design tapestries for the Sistine Chapel and continued work on St. Peter’s Basilica.
Their influence extended to church music, religious festivals, and the decoration of chapels with fine art.
Medici popes utilized their religious authority to sponsor art, shaping the appearance and significance of sacred spaces during the Renaissance.
This blending of politics, religion, and culture reinforced the Medici family’s position as a leading force in European history.
Legacy and Influence of the Medici Family Line Beyond Florence
The Medici family’s rise as a banking dynasty in Florence enabled them to influence art, politics, and culture far beyond Tuscany.
Their marriage alliances, patronage, and political strategy shaped Renaissance art, European leadership, and science for centuries.
Catherine de’ Medici and the Medici Family Influence in France
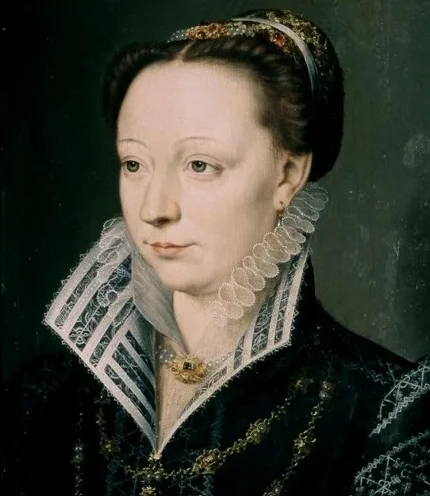

Catherine de’ Medici, a key member of the Medici family, became Queen of France in the 16th century through her marriage to Henry II.
She witnessed her country struggle with religious wars and leveraged her Florentine background and political acumen to promote peace and cultural development in France.
She introduced Italian customs, food, and art to the French court, bringing ideas from the Italian Renaissance to the French court.
Many French artists, chefs, and architects benefited from her influence, which led to changes in French fashion, gardens, and cuisine.
Catherine’s leadership helped spread Renaissance culture in France and connected two powerful royal families, strengthening the Medici’s influence across Europe.
Medici Queens and Their Role in European Political Strategy
Medici marriage alliances helped secure the family’s lasting power. Medici queens, such as Catherine de’ Medici and Marie de’ Medici, married into European royalty and linked the Medici family with the ruling houses of France and Spain.
These Medici queens used marriage and kinship as political tools. They shaped foreign policy and promoted the interests of Florence and the Medici family beyond Italy.
Their involvement in European courts allowed the Medici to influence not only art and culture but also government, religion, and international treaties.
List: Key Medici Queens
- Catherine de’ Medici (Queen of France)
- Marie de’ Medici (Queen of France)
Medici Family Legacy: From Banking Family to Political Dynasty
The Medici started as bankers in Florence. They lent money and managed investments for kings, popes, and merchants across Europe.
Their banking success gave them wealth and power. They controlled politics in Florence, sponsored Renaissance artists, and built alliances with other powerful families.
The Medici family became a political dynasty over time. They produced four popes and two French queens.
Medici rulers controlled Florence and Tuscany. They influenced decisions across Europe.
Their wealth enabled them to construct grand palaces and acquire fine art. They commissioned works from artists like Michelangelo and Botticelli.
| Key Roles | Notable Members |
|---|---|
| Bankers | Cosimo de’ Medici |
| Rulers | Lorenzo de’ Medici |
| Popes | Leo X, Clement VII |
| Queens | Catherine, Marie |
The Fall of the Medici Dynasty and Its Cultural Aftermath
The Medici dynasty began to fall in the 18th century. Internal struggles, costly wars, and a lack of male heirs all contributed to weakening the family.
The last Medici ruler died in 1737. After this, Tuscany passed to the House of Lorraine.
After their fall, support for Renaissance art in Florence slowed. Many Medici treasures remained in Florence, resulting in renowned collections like those in the Uffizi Gallery.
The Medici legacy continued to shape Florence and the Italian Renaissance. Their influence made Florence a center for art, learning, and innovation.
Medici Patronage of Science and Its Long-Term Cultural Impact
The Medici also supported science. Cosimo I and other family members supported scientists such as Galileo Galilei by providing them with funds, shelter, and public recognition.
They built libraries and encouraged study in math, astronomy, and medicine. During the Italian Renaissance, Florence emerged as a hub for scientific discovery.
These efforts helped advance science and technology across Europe. The Medici showed that wealth and power could drive innovation.
Key examples of Medici contributions include:
- Funding astronomical research
- Building the Laurentian Library
- Supporting scientific gatherings and debate
Frequently Asked Questions
The Medici family played a key role in Florence during the Renaissance. Their influence touched banking, politics, art, and culture across Europe.
Is the Medici bloodline still existing?
The main Medici family line ended in the 18th century. Distant relatives may still exist, but the direct descendants who ruled Florence and Tuscany died out with Anna Maria Ludovica de’ Medici in 1743.
Today, there is no ruling on the Medici heir.
How is Catherine De Medici related to Cosimo De Medici?
Catherine de’ Medici was the great-granddaughter of Lorenzo the Magnificent. Lorenzo was the grandson of Cosimo de’ Medici, making Catherine a direct descendant of Cosimo.
What happened to the Medici family line?
Over the centuries, the Medici family’s power declined due to financial difficulties, a lack of heirs, and political shifts. Their official line ended in the 1700s after centuries as Florence’s leaders and influential patrons of art and science.
Were the Medici family royalty?
The Medici were not born into royalty, but later became dukes of Florence and grand dukes of Tuscany. Some family members became popes and married into other royal families, which increased their power.
Who inherited the Medicis’ wealth?
After the last Medici died, much of their wealth and art collections went to the city of Florence. Anna Maria Ludovica de’ Medici arranged for the family’s art treasures to remain in Florence, benefiting the city and its museums.
Those collections are still on display today.
Does the Pazzi family still exist?
The Pazzi family, known for the failed conspiracy against the Medici, still has descendants in Italy. Although they never regained their former influence, members of the Pazzi family continue to reside there.
Did the Medici family go broke?
The Medici bank, once the most powerful in Europe, suffered significant financial losses in the late 15th century due to risky business decisions and mismanagement. Later, the Medici still had wealth and land, but their power faded as fortunes declined and other families rose.
Who was the most powerful family in Italy?
During the Renaissance, the Medici family was the most powerful in Florence and had a profound influence in Italy. Families like the Sforza in Milan and the Borgia in Rome were also influential, but few matched the Medici in politics, banking, and the arts.
Why were the Medicis so hated?
Some Florentines resented the Medici for using their wealth and banking power to control politics. They often clashed with rival families and faced conspiracies, such as the Pazzi plot.
Their actions led to distrust and opposition, especially from those who lost influence.
How much would the Medici family be worth today?
It isn’t easy to estimate the Medici family’s wealth in today’s terms. Historians suggest that they would have been worth hundreds of millions or even billions in modern currency at their peak.
Their wealth funded art and architecture across Europe. They also used their resources to build political alliances.



 Leonardo Bianchi,
the creator of Leonardo da Vinci's Inventions.
Thank you for visiting
Leonardo Bianchi,
the creator of Leonardo da Vinci's Inventions.
Thank you for visiting