
Leonardo da Vinci‘s impact on the Renaissance still fascinates people today. Many wonder how one person could shape such a significant era.
You are not alone if you have ever wondered whether his ideas and work influenced others. In this post, you will get clear answers about his impact and learn what sets him apart from his peers.
Leonardo da Vinci’s influence on the Renaissance reached far beyond painting. He inspired new thinking in both art and science.
He became a role model for other artists and inventors, showing how creativity could work in tandem with curiosity and observation.
You’ll discover how his experiments and studies in anatomy, engineering, and natural science helped shape future generations of humanists and thinkers.
By looking at specific examples, you’ll see how da Vinci’s skills and discoveries made others believe that they, too, could blend art and science to create something new and meaningful.
To understand the full reach of his influence, follow along as this article further explores his inventions, sketches, and bold ideas.
The Leonardo da Vinci Impact on the Renaissance and Its Artistic Innovation
Leonardo da Vinci shaped the Renaissance by combining artistic innovation with scientific inquiry. His mastery of painting techniques, empathy in art, and curiosity about the natural world set new standards for artists and thinkers.
Leonardo da Vinci’s Genius and Artistic Innovation in the Renaissance
Leonardo da Vinci’s impact on the Renaissance came from his unique combination of creativity, observation, and intellect. Known as a true Renaissance man, he excelled in painting, anatomy, engineering, and architecture.
He merged these fields through a multidisciplinary approach. He filled dozens of notebooks with sketches and questions inspired by nature, science, and inventions.
This process made him a pioneer in both artistic and scientific observation. His anatomy and physiology studies deepened his understanding of the human figure, improving art and medicine.
Leonardo’s blend of imagination and reason helped drive advances in painting and science. His vision inspired other artists and scientists to experiment and innovate.
Masterpieces Like Mona Lisa and The Last Supper Shaping Renaissance Art
Leonardo’s famous works, including the Mona Lisa and The Last Supper, marked key moments in Renaissance art. These masterpieces showcased advanced painting techniques and brought new depth to portrait and religious painting.
The Mona Lisa stands out for its soft transitions between light and shadow, natural landscape, and mysterious expression. The Last Supper uses perspective, gesture, and composition to tell a biblical story with clarity and emotion.
Both paintings use detailed observations of nature and human emotion to achieve lifelike results. Leonardo’s masterpieces have been studied and admired for centuries.
During the Renaissance, they established high standards for skill, realism, and artistic innovation in portraiture and storytelling.
Painting Techniques and the Use of Light and Shadow (Chiaroscuro)
Leonardo introduced pioneering painting techniques during the Renaissance. He perfected chiaroscuro, contrasting light and shadow, to model form and create three-dimensional effects.
This method made figures appear more lifelike and scenes more dramatic. He also used sfumato to blend colors and tones without harsh lines, giving paintings a soft, realistic look.
These techniques brought out subtle details in skin, fabric, and landscape. Leonardo’s approaches influenced other artists to experiment with light, perspective, and composition.
Many painters adopted his methods, spreading his legacy and raising the quality of Renaissance art across Europe.
Creativity, Empathy in Art, and the Philosophy of Art During the Renaissance
Leonardo da Vinci believed that art should show what people look and feel. He focused on empathy in art, giving paintings a sense of soul and emotion.
This made viewers connect with his subjects on a deeper level. He believed that art and science are linked.
Observing the natural world and understanding human anatomy made art stronger and more prosperous. This belief reflected the Renaissance goal of connecting different fields and valuing direct observation.
Leonardo inspired artists to pay attention to emotions, nature, and realism. His ideas still shape art and art education today.
Influence on Later Generations Through Art and Artistic Innovation
Leonardo’s influence stretched far beyond his own time. Later artists studied his sketches, scientific notebooks, and paintings for inspiration.
His mastery of multiple fields showed the power of a multidisciplinary approach. Architects and engineers learned from his studies of structure, urban planning, and inventions.
Leonardo da Vinci’s methods of scientific observation and detailed recording of the natural world became models for art and science. His impact led to advances in anatomy, perspective, and artistic innovation.
Today, he is recognized for creating new standards in art, science, and technology that shape modern thinking and practice.
Leonardo da Vinci Impact on the Renaissance in Science and Multidisciplinary Studies
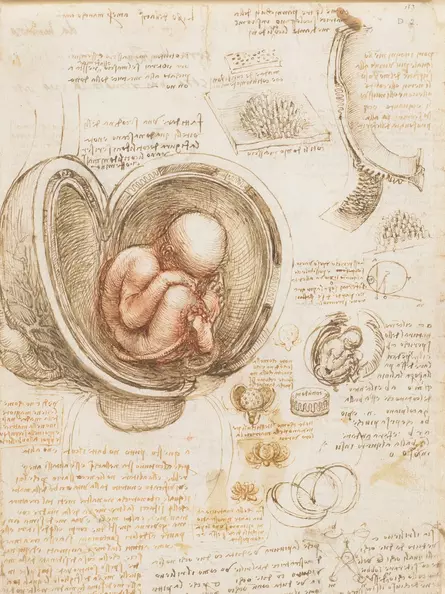
Leonardo da Vinci shaped the Renaissance with his innovative approach and mastery across many fields. His commitment to blending science and art changed how people understood the natural world.
His careful studies, sketches, and inventions showcase a dedication to observation and experimentation.
Anatomy Studies and Scientific Inquiry: Bridging Art and Science
Leonardo da Vinci’s anatomy studies transformed artistic and scientific understanding during the Renaissance. He dissected human and animal bodies to learn how muscles, bones, and organs work.
These explorations helped him create more lifelike paintings and advanced knowledge of anatomy and physiology. He drew hundreds of sketches showing the structure and movement of the human body.
Using careful observation, he revealed how different parts connected and functioned. Leonardo’s notebooks, filled with labeled drawings and notes, allowed later artists and doctors to learn from his discoveries.
His blend of art and scientific inquiry became a key example of the Renaissance humanist ideal. Today, his anatomy studies are considered a bridge between the arts and sciences.
Observation, Empiricism, and Detailed Study of Nature in Leonardo’s Work
Leonardo approached nature with precise observation and a belief in direct experience, also known as empiricism. He watched how light and shadow played across objects, water moved, and plants grew, recording these observations in his sketchbooks.
This focus on scientific observation led him to discoveries and made his art more realistic. He wrote down what he saw and tested ideas by drawing them from different angles using correct perspective and proportion.
Leonardo’s work often explored the natural world down to tiny details like the patterns of leaves or the anatomy of birds’ wings. His scientific curiosity led him to ask questions and seek answers by watching, sketching, and sometimes conducting small experiments.
This dedication to careful study was rare in his time but became central to the later scientific method. Leonardo’s legacy as a pioneer of natural observation and empiricism shows how he inspired future scientists and artists to trust their careful study of the world around them.
Engineering, Inventions, and Technological Advancements of a Renaissance Visionary
As a Renaissance visionary, Leonardo did not limit himself to painting and drawing. He designed bridges, war machines, flying devices, and urban planning and architecture tools.
While not all were built during his life, he drafted blueprints for inventions that demonstrated creative ideas far ahead of his era. Leonardo’s sketches include machines like an early helicopter, a mechanical knight, and advanced water pumps.
He explored urban design, imagining new ways to make cities healthier and safer. His drawings often showed how each device part would move, using his deep knowledge of mechanics and physics.
These inventions had a lasting impact. Later, engineers used his sketches and ideas to build similar machines.
Leonardo’s constant drive for technological advancements and innovation reinforced the Renaissance ideals of curiosity, creativity, and progress.
Integration of Art and Science Through Sketches, Notebooks, and Experimentation
Leonardo’s many notebooks are filled with sketches, scientific diagrams, and experimental notes. He recorded both artistic studies and scientific observations, making these notebooks a remarkable record of his multidisciplinary approach.
He often used drawing to solve problems, plan inventions, and test theories. His notebooks explored subjects like light and shadow (chiaroscuro), anatomy, geometry, and principles of architecture.
Leonardo constantly experimented, mixing paints, trying new materials, and testing new painting techniques to increase the realism in masterpieces like the Mona Lisa and The Last Supper. Integrating art and science in Leonardo’s work encouraged later thinkers to value creative imagination and critical observation.
His sketches show how art can be a method for discovery and how scientific methods can improve artistic results.
Legacy and Influence on Later Intellectual and Multidisciplinary Approaches
Leonardo da Vinci’s legacy shaped the history of art, science, and the spirit of the Renaissance. His multidisciplinary approach inspired later generations of intellectuals, artists, and scientists to pursue knowledge across fields.
Leonardo’s notebooks, inventions, and masterpieces set new standards for creativity and investigation. His blending of observation, experimentation, and artistic expression models the Renaissance ideal of a “universal genius.”
Today, Leonardo da Vinci is frequently recognized as an early master of interdisciplinary studies. His work inspires those interested in innovation and integration across fields even centuries later.
The Broader Cultural and Philosophical Impact of Leonardo da Vinci on Renaissance Ideals
Leonardo da Vinci’s influence on the Renaissance shaped not just art and science, but also new ways of thinking about humanity’s place in the world. His ideas and creations set standards for creativity, observation, and innovation, inspiring artists and thinkers of his time and future generations.
Humanism and the Renaissance Humanist Ideal in Leonardo’s Philosophy
Leonardo da Vinci approached the world with deep curiosity and respect for the individual. He believed in the importance of direct observation and hands-on experience rather than blindly accepting traditional ideas.
This curiosity reflected Renaissance humanism—the belief in the value and dignity of people and the power of human achievement. He saw nature as a model of perfection.
For Leonardo, understanding nature and applying this understanding through art or science showed respect for the world’s harmony and beauty. His writings and sketches blend scientific observation with the humanist drive to learn.
Through these efforts, Leonardo became known as a true Renaissance man.
Contributions to Architecture, Urban Planning, and Cartographic Studies
Leonardo made important contributions to architecture, urban planning, and cartography. He designed buildings, bridges, and ideal cities focused on better living spaces and public health.
His detailed designs appear in his notebooks, where he drew new fortifications and advanced city layouts that used flowing water for cleanliness.
He improved maps and geographical drawings, raising standards for accuracy and detail. Leonardo used careful observation in his cartographic studies, setting the stage for later scientific mapping.
His inventive plans and maps advanced urban design and cartography during the Renaissance.
Perspective, Proportion, and Pioneering Techniques in Renaissance Art and Science
Leonardo da Vinci transformed art by studying light, shadow, perspective, and proportion. He used chiaroscuro to blend light and dark for realism and sfumato to create soft transitions between colors.
These methods made his paintings unique and influenced artists across Europe. He studied the human body closely, carefully drawing muscles, bones, and organs.
His anatomy studies helped artists and doctors understand how the body worked and moved. Masterpieces like the Mona Lisa and The Last Supper show his natural poses, lifelike perspective, and accurate anatomy.
Speculation, Philosophy, and the Intellectual Spirit of the Renaissance
Leonardo embraced speculation and the search for truth. He asked questions about everything he saw, from water flow to birds’ flight, and tested his ideas through experiments and study.
This mix of philosophy and investigation drove much of his work. He saw connections between different subjects, linking art, science, nature, and invention.
By viewing the world as patterns and relationships, he encouraged interdisciplinary studies. His intellectual spirit reflected the Renaissance’s openness to exploring new knowledge.
Leonardo’s Lasting Legacy in Shaping Renaissance Ideals and Influence on Future Generations
Leonardo da Vinci’s visionary work continues to inspire people today. His notebooks and sketches reveal a genius who pushed for innovation in engineering, architecture, medicine, and painting.
He helped define the Renaissance thinker by mastering many subjects and embracing creativity. Future artists, scientists, and inventors built on his foundations, adopting his careful observation, creative problem-solving, and fearless experimentation.
The interdisciplinary approach he modeled guides modern education and research. His legacy remains central to the Renaissance and beyond.
Frequently Asked Questions
Leonardo da Vinci shaped art and science during the Renaissance and inspired generations. His studies and achievements influenced Western history, education, and creative expression.
What impact did Leonardo have on the Renaissance?
Leonardo da Vinci changed painting by using perspective, shading, and anatomy to create lifelike images. He contributed ideas in engineering, architecture, and science, moving Renaissance culture toward careful observation and experimentation.
His work encouraged other humanists and artists to explore science and art together.
How did art impact the Renaissance?
Art in the Renaissance reflected a growing interest in realism, emotion, and the human body. Artists like Leonardo used scientific discoveries to make their paintings and sculptures more natural and detailed.
Art inspired people to think about new ideas and helped spread knowledge throughout Europe.
What is the influence of Leonardo da Vinci?
Leonardo’s impact stretches across many fields. He is seen as a founder of the High Renaissance style and inspired artists to strive for naturalism and harmony.
Leonardo’s scientific studies encouraged others to ask questions and experiment. His influence appears in painting, science, engineering, and anatomy.
Why was Leonardo da Vinci considered a Renaissance person?
Leonardo was called a Renaissance person because he had skills in many areas. He was not just a painter but also an inventor, scientist, and engineer.
His interests and talents included art, science, technology, and more, showing the era’s wide-ranging curiosity.
Why was Leonardo da Vinci important to the Renaissance quizlet?
Leonardo da Vinci is important in history lessons about the Renaissance, especially his masterpieces in painting and his scientific inventions. He is often mentioned for his creativity and intelligence and for setting new standards in art and research.
His work appears in many educational resources.
Which artist most embodied the spirit of the Renaissance?
Leonardo da Vinci is often seen as the artist who best embodied the Renaissance’s ideals. He combined creativity, curiosity, and innovation, excelling in many subjects.
Michelangelo and Raphael were also leading figures, but Leonardo’s broad interests, as seen in his notebooks and artworks, set him apart.
How did the Mona Lisa impact the Renaissance?
The Mona Lisa introduced a new way to paint portraits with lifelike details and a realistic expression. Its use of light, composition, and subtle smile made it a model for other artists.
The painting is studied for its techniques and has become one of the period’s most famous works.
What did Leonardo da Vinci do in his early life?
In his early life, Leonardo worked as an apprentice in Florence. He learned drawing, painting, and sculpture from masters in the city.
These years gave him the skills and knowledge he used in his later artwork and inventions.
What were the effects of the Renaissance?
The Renaissance brought advances in art, science, music, and literature. It led people to question old beliefs and value education.
Many inventions and discoveries from this era changed Europe and had a lasting impact on the world.
What did Leonardo da Vinci do in Florence?
While in Florence, Leonardo da Vinci created early works, such as sketches and paintings, and worked on engineering projects.
He studied with local masters. Leonardo designed inventions in his notebooks.
His time in Florence helped him develop his artistic style and expand his scientific interests, making him a key figure of the Renaissance.

 Leonardo Bianchi is the founder of Leonardo da Vinci Inventions & Experiences, a travel and research guide exploring where to experience Leonardo’s art, engineering, and legacy across Italy and Paris.
Leonardo Bianchi is the founder of Leonardo da Vinci Inventions & Experiences, a travel and research guide exploring where to experience Leonardo’s art, engineering, and legacy across Italy and Paris.